kpi table in excel examples. Kpi remuneration system - its features
Key performance indicators KPI (Key Performance Indicators) - a term that came to us from Western system management. Companies in America and Europe have been using this performance analysis tool for decades.
KPI allows not only to analyze, but also to control the activities of employees, departments and the company as a whole.
What key indicators efficiency and examples of KPIs will be discussed in this article.
Key performance indicators KPI - what is it?
People make more efforts when they believe that they are justified and will help achieve the desired goal.
IMPORTANT: Motivation at the enterprise is built in such a way that the goal of the company itself is achievable through the achievement by employees of their goals.
Of course, employees must understand the purpose of the enterprise and how they can influence it, as well as what they receive as a reward for excellent work done to achieve the goal (for example, a bonus to their income).
That is why middle and senior managers often receive bonuses in addition to their basic salary.
How are
KPI is not a system built on motivation, but just one of the management tools in an enterprise. The peculiarity of this management tool is that employees from different departments in the company meet key performance criteria.
In order to build a KPI system in an enterprise, it is necessary not only to create the list of indicators itself, but also to describe how they will be calculated, as well as create reporting forms for such indicators.
The first thing a director or shareholders should do is to re-formulate the long-term and short-term goals that the company is striving for.
Based on these goals, criteria are built, combined into a subsystem, and then into a KPI system. After the KPIs are defined, the manager will need to allocate responsibility for their implementation.
Their types
 All key criteria can be divided into two large groups:
All key criteria can be divided into two large groups:
- lagging;
- operational.
The first show the result at the end of a certain period. So, for example, most financial indicators are specifically lagging, because they can reflect the potential of the company, but they cannot convey how things are in the company for a specific period of time.
Operational indicators can be adjusted during the reporting period in order to achieve the desired results at the end of it. By such indicators, one can judge how things are going in the company for a specific period, and also by them one can predict what to expect in the future.
Moreover, operational indicators make it possible to judge whether the company's customers are satisfied, as well as how well the business processes in the organization are debugged.
Key indicators differ by type:
- indicators result- demonstrate the quality of the result, as well as the ratio of its actual quantity to the expected one;
- indicators costs- show the amount of expenses incurred;
- criteria functioning- most often they show how the algorithm of a particular business process corresponds to the required one;
- criteria performance- show the ratio of the result to the resources spent on its acquisition;
- indicators efficiency- as well as the previous indicators, this group of criteria refers to production estimates and demonstrates the relationship of the result to the amount of resources spent to achieve it.
How the system works
The KPI system is based on two theories: control and management according to goals. The essence of the system is that the company has the opportunity to plan and foresee the result by meeting certain indicators.
The KPI system is primarily designed to ensure that the staff, as they fulfill their direct duties, do not forget that the company has global goals and that if they put their efforts to achieve them, they will be rewarded. Most often, bonuses and other monetary incentives act as remuneration.
Video - how to implement a KPI system in a company:
Currently, such a system is recognized as one of the most effective systems for motivating employees, as well as stimulating their work activities. Of course, first of all, this system applies to management personnel, for example, middle and senior managers, as well as managers, economists and all those who have a direct impact on the company's profits, as well as its positioning in the market.
In sales
As a rule, in most sales departments it is customary to reward managers for achieving individual indicators. So, you can even meet whole nominations, for example, “seller of the year”.
Of course, such rivalry sometimes does not benefit the team, because “salespeople” begin to work not for the team, but for themselves, therefore collective stimulation and rewarding is recommended.
Key criteria in sales are calculated based on financial indicators, for example, such as:
- sales profit;
- production cost;
- revenue;
- inventory value, etc.
In production
Most often, when implementing KPI in production, the management of the enterprise faces two tasks: to keep production volumes, and also to maintain quality at the position level.
So, in production can be introduced the following types premiums:
- achieving or exceeding the volume of output;
- no more than any specific number of claims from buyers per unit of time;
- percentage of defective products.
Of course, these are not the only criteria that can be evaluated, and depending on the type of product and production volume, the management of the enterprise can implement a completely different KPI system.
In the service sector
The service sector assumes the presence of the largest number of key indicators. So, for example, you can select performance criteria that include the number of sales per day, month, week and year, order size, comparison of the number of orders a month, quarter or year ago with the current indicator, and so on.
Marketing in the service sector also did not remain without the use of KPI. The following criteria are distinguished:
- the quantity and quality of reviews for the service;
- the number of clients who have become permanent;
- the number of subscribers to the company's page in social networks;
- advertising return rates;
- the number of letters received from buyers;
- the time for which one request is solved;
- efficiency affiliate programs and so on.
IMPORTANT: As a rule, in a company in which KPI practice has become a daily norm, constant monitoring of the implementation of key performance indicators becomes the norm.
After some period of time from the introduction of practice to its successful execution control over it becomes a routine. All subsequent decisions are usually made on the basis of these indicators.
Examples of KPIs
Depending on the position, scope of work, stage life cycle organization and other important KPI indicators for all employees will be different.
So, for a marketer, this will be the share occupied by the company in the market, and for an accountant, it will be the timely conduct of operations to pay taxes, transfer wages and so on.
Consider key performance indicators on specific examples.
For manager
Management is a very flexible concept and therefore there are no indicators that could be used both in sales management and, for example, in advertising. Consider the main types of management and KPI.
By sales
Most modern companies today have such a KPI system installed, in which sales managers receive a stable salary, as well as a bonus based on the results of sales.
Such a system is quite understandable and transparent, however, it also has some disadvantages. For example, each "salesperson" works exclusively for himself, forgetting about the team, moreover, the quality of service with such an established KPI system suffers greatly, since management is aimed solely at increasing sales.
Video - Key Performance Indicators KPI for Sales Manager:
An alternative to such a KPI system has become a system that combines several indicators. So, in order to calculate the effectiveness of a person in the sales department, it is necessary not only to find out how many purchases he helped customers make, but also how satisfied they were with the purchase.
Procurement
The functionality of a purchasing manager varies greatly depending on the field of activity of the company. In its most simplified form, it is simply the selection and purchase of goods.
The maximum possible areas of responsibility of the purchasing manager are:
- Inventory Management;
- work of purchases;
- price analysis;
- product promotion;
- launch of new product lines.
KPI indicators for a purchasing manager include not only economic indicators, but also qualitative, i.e., the criteria for the activity of a manager.
So, when calculating KPI, you can use:
- timeliness of payment to suppliers;
- no delays in placing an order;
- analysis of prices for goods from competitors;
- launch of new product lines.
Advertising
Depending on the volume of tasks performed, the direction of the company, as well as the skills of the advertising manager, the following are encountered: KPI indicators in advertising management:
- efficiency advertising campaigns;
- effectiveness of promotions;
- merchandising;
- the number of new customers of the company;
- efficiency of work with Internet platforms and social networks.
In trade
Key criteria in retail may or may not be financial. Retail KPIs should be used all the time as they make life much easier for any retail organization. The analysis of indicators will help not only to determine the company's further goals, but also to identify all the existing shortcomings in the existing business model.
For a grocery store clerk
The indicators by which you can evaluate the work of the seller of a grocery store are the following:
- sales growth;
- sales volume per physical unit (for example, per 1 sq. m. of area trading floor or window length)
- sales volume per 1 performed operation;
- sales volume for 1 hour of work.
Also, in addition to the above indicators, you can use such a value as the efficiency of using goods. Inventory efficiency involves calculating the ratio of net sales over time to inventory.
For the seller of non-food products
For the seller not food products some indicators similar to those for a grocery seller may be involved. So, it can be the sales volume for 1 hour of work. In addition, the following criteria should be taken into account:
- average purchase receipt;
- the number of returns for a certain period of time;
- wage criterion.
For other professions
Sometimes the KPI system is introduced not only for the management team, but also for people involved in the sales process, but also for other employees of the company.
For employees involved in production, the key performance criteria will be, for example, the growth of labor productivity, the relative release of workers, wage intensity, as well as the increase in production due to increased productivity.
The main performance indicator accountant is the payment of all basic payments on time, as well as an indicator of interaction with tax authorities and extra-budgetary funds.
For lawyer the main performance indicators will be the percentage of claims closed in pre-trial order by the company's counterparties, as well as the percentage of cases won in court.
Conclusion
KPIs are performance indicators for an organization. created to achieve its goals. Performance indicators are an indicator of what success the company has achieved at a certain stage of its activity.
In order to develop and implement such a system in an organization, it is first necessary to define goals, on the basis of which a list of performance indicators will already be built.
In addition to compiling the list, the head of the organization should appoint responsible persons, as well as determine the form of reporting on indicators.
Depending on the direction of the company, its stage of the life cycle, as well as other important indicators, the KPI of employees can be completely different.
So, for one advertising manager, only one efficiency criterion will be valid - the effectiveness of advertising campaigns, for another advertising manager, in addition to this criterion, a criterion for working with promotions will be introduced in social networks etc.
Optimal conditions for opening and maintaining a current account for entrepreneurs
KPI-based personnel are gaining more and more popularity in Russia. The main advantages of such mechanisms are in the rational reflection of the activities of companies.
KPI: what is it
KPI (KPIs) is the English abbreviation for “key performance indicators”, in Russian it is referred to as KPIs - key performance indicators (sometimes parameters). But in the original foreign sounding it is used as a norm. KPI is a system that allows you to evaluate the performance of the company's employees in order to achieve goals (strategic and tactical).
"Key indicators" allow the company to analyze the quality of its structure, the potential in solving problems. On the basis of KPI, a system of the most important factor is also formed: if there are no signs of targeting, then there is nothing to apply to “key indicators”. and KPI, thus, are two interrelated phenomena. The first involves, first of all, forecasting the results of work, as well as planning how these results will be achieved.
Who came up with KPI?
An unequivocal answer to this question history does not give, however, one can trace how the world management went to understand KPIs, what they are and why they are useful. In the late 19th and early 20th century, the sociologist Max Weber determined that there were two ways to evaluate the work of employees: the so-called "sultanic" and meritocratic. According to the first, the boss (“sultan”) at his own discretion assessed how well a person copes with his duties. The rational principle here plays a secondary role, the main thing is a purely emotional perception of the work of a subordinate.

The meritocratic method is when the results of labor are evaluated according to real achievements, with the involvement of objective measurement mechanisms. This approach was adapted by management theorists in Western countries and gradually crystallized into what we know as the KPI system. An important role in systematizing the rational evaluation of personnel performance was played by the works of Peter Drucker, who is considered to have turned management into a scientific discipline. The concepts of the scientist directly state that there are goals, but there is an assessment of the degree of their achievement through key performance indicators.
Benefits of KPIs
home positive side KPI systems - the presence of a transparent mechanism for all employees of the company to evaluate the work and work of the enterprise as a whole. This allows the authorities to evaluate the performance of all subordinate structures in real time, predict how tasks will be solved and goals achieved. The next plus of KPI is that the management has a tool for adjusting the work of subordinates if the current results lag behind the planned ones.

If, for example, performance measurement in the first half of the year reveals that performance is not high enough, then workshops are held to identify the reasons and encourage employees to perform better after the next six months. Another positive side of KPI is the feedback between the specialist and the manager. The first will receive not just instructions and sometimes seemingly biased nit-picking, but well-founded comments, the second will improve performance by specifying errors and shortcomings in the work performed by the subordinate.
Cons of KPIs
The results of assessments within the framework of KPIs (performance indicators as such) can be interpreted not quite correctly, and this is the main drawback of this system. As a rule, the probability of occurrence of such a problem is the lower, the more attention is paid at the stage of formation of criteria for how to evaluate performance parameters. Another disadvantage of KPI is that companies will have to spend a lot of resources (usually calculated in time, labor and finance) to implement this system. We are talking, of course, about working on the key parameters of the effectiveness of the proper level of elaboration. There is a possibility that it will be necessary to carry out large-scale retraining of employees: specialists - with a view to changing tasks, and hence working conditions, while management will have to master new methods for assessing the work of subordinates. The firm may not be ready to give the team extra time to learn new things.
Subtleties of KPI implementation
The main task when implementing a KPI system (“from scratch”) is to prevent a negative attitude towards it from employees. Therefore, the management of the company needs to clearly convey the meaning and practical benefits of innovations to each of the subordinates, whose work is subject to subsequent evaluation for effectiveness. The best method here, according to some experts from the field of HR, is an individual presentation, an explanation to specialists in specific positions: KPIs - what are they and why implement this system in a company.

It would be a mistake to unconditionally impose efficiency parameters by order, but the necessary step is an appeal from the top officials of the company. If, for example, a line manager informs subordinates in his department about the imminent implementation of KPI, then this information should also be confirmed by the CEO. The specialist must understand that the system of key performance parameters is not an invention of the boss, but an element of the strategic policy of the entire company.
Optimal timing of KPI implementation
Among experts, there is an opinion that KPI indicators, if we are talking about a system, should be implemented simultaneously at all levels of company management - from ordinary specialists to top managers. According to this point of view, the timing of the implementation of key performance indicators cannot be extended in time: the system starts working immediately. The only question is how to optimally choose the moment of its launch. There is a point of view that it is enough to notify employees about the start of KPI about three months in advance. This is enough for the company's staff to study the specifics of the future assessment of the effectiveness of their work.

There is also the thesis that for some time KPI can work in parallel with the previous payment system. Depending on the degree of liberalism of the authorities, the employee will be able to choose according to which scheme he will be paid. It is possible to fully motivate a person to work according to the new KPI through bonuses and bonuses, the conditions for obtaining which will be clearly spelled out in the key parameters.
Stages of creating a KPI system
Actually, as such, the introduction of KPI mechanisms is preceded by several stages preparatory work. Firstly, this is the period associated with the formulation of strategic goals that are set for the company. As part of the same stage of work, the general concept is divided into tactical areas, the effectiveness of which is to be measured. Secondly, it is the development of key performance indicators, the definition of their essence. Thirdly, this is work on the distribution of official powers related to the implementation of the system, so that each person in charge asks a question like “KPIs - what are they?”

Thus, all indicators will be assigned to specific individuals (divisions) in the company. Fourth, current business processes may need to be adjusted (if the updated strategy requires it). Fifthly, it is the development of a new system, the creation of payroll formulas according to fresh criteria. After completing all of the above procedures, you can start the KPI system.
KPI Requirements
As mentioned above, KPIs are key performance indicators that are inextricably linked to the company's goals. The quality of targeting development is the main requirement for the KPI system. Goals can be formed according to different principles, but one of the most popular in the HR environment is the SMART concept. Means "specific" (specific), "measurable" (measurable), "achievable" (achievable), "relevant to the result" (relevant), "time-bound" (time-bound), and, as a result, giving worked out and quality KPIs.

Examples of goals that meet these criteria: "open so much (measurable) outlets(specific) in the city (relevant) in the first quarter (time-bound)”, or “sell so many air tickets to such and such a country in three weeks”. Each goal should be divided into tasks, which, in turn, are reduced to the level of personal KPIs (for employees or departments). The optimal number, according to some experts, is 6-8.
KPI Automation
One of the factors for the successful implementation of KPIs is the technological infrastructure. Since key performance indicators are a set of rational indicators, a computer will do a very good job with them. There are many software solutions to manage KPIs. The possibilities available in such distributions are quite extensive. Firstly, it is a convenient presentation of information (in the form of graphs, analytics, documentation) about the processes associated with KPIs. What does it give? Mainly, the unity of data perception, reducing the likelihood of misinterpretation of numbers. Second, the collection and calculation of performance indicators. Thirdly, this is a multidimensional (with very large volumes of numbers) analysis, which will be difficult for a person without a program to perform. Fourth (if there is a network infrastructure), this is the exchange of information between individual employees and the establishment of channels feedback"boss-subordinate".
KPIs are key performance indicators that evaluate the work of each employee. They also help to analyze the work of the entire company, achievements for a certain period and are an excellent motivator to quality work. The main thing is the correct development of a KPI system for a specific position, taking into account all the nuances of an employee's activities in the company.
Universal performance indicators cannot be applied to all positions, because they just can't meet expectations. Let's say it's almost impossible to make a KPI for an accountant. The development of a motivation system based on KPI is an analytical work that includes both the preparation of KPI and the analysis of the result.
It is important to consider the following:
- There should be few performance indicators, otherwise the calculations will be confusing and, as a result, the goal of the assessment will not be achieved.
- Each KPI must match the final goal.
- The established KPI indicators must be guaranteed to be achievable and clearly correspond to the sphere of influence and responsibility of the employee (position).
- It is possible and necessary to prescribe employee motivation only on the basis of key performance indicators, then the employee will understand what is expected of him and will move towards a clear goal.
What indicators are
Often in companies and enterprises, KPI indicators are classified as operational and those that are late with the result.
Long-term indicators show the result after a certain period of time, in turn, operational (leading) indicators allow you to evaluate the effectiveness of work very quickly.
Varieties of indicators in business processes:
- Result performance indicators are KPIs of profit, revenue and sales for a specific period.
- Cost KPIs - help evaluate the achievement, taking into account financial and time costs.
- Performance indicators reflect the correctness of the employee's activities, his system of work in accordance with the regulations and algorithms of his position.
- Efficiency KPIs show the level of the ratio of the result to the cost of it in different options.
- The productivity efficiency ratio gives an understanding of the result achieved in a certain ratio with the time spent.
When calculating KPI, you should immediately form the goal and priorities for the selected position. In each case, they are calculated separately, depending on the scope of the company. The assessment methods and the specific calculation formula for a competent assessment of the results depend on this.
We calculate KPI indicators
To understand the picture of developing KPI indicators, we will give an example that indicates the algorithm of actions.
Stages of developing KPI indicators:
- Formation of the team, selection of members of the working group and research for each position.
- Drawing up a methodology of actions. Based on the analysis, models of the system of performance indicators for positions are created, regulations are prescribed, indicators are developed and tested.
- Implementation of the KPI system: established performance indicators are integrated into software, and employees are informed about the conditions and requirements under the signature.
- The final stage of development: monitoring the implementation of KPI, adjusting indicators during the test period.
In practice, 2 methods of developing KPIs are most often used: process and functional methods.
The process approach is based on performance indicators based on the internal business processes of the enterprise.
The functional approach relies on the very structure of production or management of the organization, functional responsibilities positions, departments, branches.
We give in the table an example of calculating two methods for developing performance indicators.
| process method | functional method |
| Business process goal (sales) | |
| The dynamics of the emergence of new customers (specific number) | Profit Profitability Growth of assets in the company |
| Business process goal (performance) | |
| Dynamics of increase in the turnover of cash reserves in relation to the previous period | Number of loyal customers Sales volumes for the period in monetary terms |
| Business Process Goal for Customer Satisfaction | |
| Minimizing the number of product returns Reducing the time of the order (ordering and bringing to purchase) |
Number of new clients Reduced time to serve one customer |
| The purpose of the HR business process | |
| Quick selection of new managers | The percentage of closed and open vacancies for a specific period |
For example
An example of calculating KPI for one employee is given in the table of the sales manager, where there is an indicator index.
https://yadi.sk/i/jomsvYOq3Kyb2z
From this example and the KPI index, we can see that this sales manager exceeded the plan by 6% and, accordingly, he is entitled to the reward agreed in his motivation.
To calculate the KPI of a position, you can use several performance indicators and calculate the motivation using the formula:
Salary + K1 + K2 + K3. Where K1, K2, K3 are KPI indicators (manager's salary + fixed % of sales + % of the number of attracted customers for the period (month) + agreed bonus for quality service clients).
So in a simple way you can enter any KPI indicators into the formula, which can be calculated as a result.
Eventually
To calculate the effectiveness of an employee's work, it is necessary to carefully approach the assessment and objectives of the position, and for this it will be necessary to analyze the level of performance and sphere of influence of the employee in a particular organization. Having determined the KPI indicators, it is possible to prescribe a motivation system, on which the employee's salary will depend.
The bonus begins with an assessment, you also need to remember the basic principle: the variable part of the salary is designed to stimulate labor activity and should encourage the achievement of above-standard results. And you should always remember that the bonus is not part of the salary. After all, the deprivation of the bonus in this case creates stress, conflicts and leads to demotivation of the staff.
The performance related pay (PRP) system is based on a staff assessment procedure based on key performance indicators (KPIs). However, in order to introduce such a system into management practice, simple and reliable methods should be developed that establish a relationship between the employee's KPI values and the value of the variable part of the salary.
Personnel assessment by KPI
Earlier in our journal, a methodology for assessing personnel by KPI was published, based on a combination of the current assessment of the results and competencies of employees. Let us briefly recall its main provisions.
For each position in the organization, on the basis of the employee's service functions, two models (tables) are developed - results and competencies. The first lists all performance criteria for performance evaluation: quantitative and qualitative, individual and team. In the second - the competencies required for this position: corporate (common for all staff of the company), managerial and expert (vocational). From these two models, 5-7 key indicators (of any type) are selected to assess the results and competencies of the employee in the coming month (quarter or other reporting period - depends on the position level) and are recorded in a personal performance table (see Table 1). At the same time, competencies are “equated” with the qualitative results of the employee’s activities. Each of the selected indicators, in accordance with the priorities of the immediate supervisor, is assigned a weight - from 0 to 1 (the total weight should be 1).
Table 1. Personal performance
|
Key indicators (KPI) |
The weightKPI |
Base |
Norm |
Target |
Fact |
Partial result, % |
For all indicators, three “performance levels” are set:
1. Base - the worst admissible value ("zero" point), from which the countdown of the result begins.
2. Norm - a level that must necessarily be achieved taking into account the circumstances (for example, the situation on the market), the characteristics and complexity of the work, and the capabilities of the employee. This is a satisfactory indicator value.
3. Purpose - above-standard level to which it is necessary to aspire.
At the end of the month (quarter), the actual KPI values are evaluated. At the same time, quantitative indicators are measured on a “natural” metric scale, and qualitative indicators are measured on an ordinal 100-point scale. With its help, you can be flexible in assessing quality KPIs by setting “reference points”, for example: base - from 0 to 20, norm - from 40 to 60, goal - from 80 to 100 points. At the same time, assessments must be “deciphered” so that employees understand exactly what results internal customers expect from them.
After evaluating the actual value of KPI, a particular result of work on this indicator is determined in accordance with the formula:
This result reflects the degree of fulfillment or overfulfillment of the norm. So, if the actual indicator is below the norm, then the partial result for it is from 0 to 100%. If the “fact” exceeds the norm, then the partial result is above 100%.
After evaluating each indicator, the employee's rating is determined. To do this, particular results (in percent) are multiplied by the weight of the corresponding KPIs and added together. The result is a "weighted average" performance ratio, reflecting (in percent) the overall performance of the employee for the reporting period, taking into account the importance and actual values of all his KPIs. If the coefficient is more than 100%, this indicates a person’s high performance (above the norm), if less, it means that the norm has not been achieved for some or even all indicators, and the overall result of the work is below the established level.
Next, you should link the received estimates and the amount of the employee's bonus. To do this, it is necessary to remember the basic principle of bonuses: the variable part of the salary is intended to stimulate the labor activity of people and should encourage them to achieve above-standard results. AT Russian practice it is not uncommon for the bonus to be considered in fact as part of the salary and paid "automatically" when the plan is fulfilled. If the employee does not reach the standard indicators, then he loses the bonus in whole or in part. This practice creates nervousness, stress, conflicts and leads to demotivation of the staff. The variable part of the salary should encourage people to achieve higher results compared to the normative ones. And for the implementation of the plan, the employee should receive a salary. It is important that the fixed part of the salary remains constant! Based on these considerations, we will consider two ways to calculate the bonus if the employee's KPI estimates are known.
The first way to calculate the premium
The variable part of the salary (performance bonus) is calculated as a percentage of the official salary using the employee's performance ratio according to the formula:
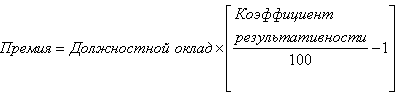
Of course, this formula is applicable only to those employees whose performance ratio is above 100%, i.e. who have reached above-standard indicators, taking into account the values of all KPIs and their weights. Otherwise, these persons do not receive the bonus. The amount of the payment is limited by the employee's bonus fund.
Consider an example. The work of the shop manager for the past reporting period (month, quarter, half year, year) was evaluated according to five key indicators (see Table 2).
Table 2. Premium calculation example (method 1)
|
Key figures |
Weights |
Base |
Norm |
Target |
Fact |
Result |
|
Volume of production |
3 million rubles |
5 million rubles |
6 million rubles |
5.5 million rubles |
||
|
Share of defective products |
||||||
|
150 thousand rubles |
90 thousand rubles |
60 thousand rubles |
75 thousand rubles |
|||
|
Performance ratio: |
||||||
|
Job salary: Performance Award: |
||||||
Suppose that the official salary of the head of the shop is 40,000 rubles. Then his bonus based on the results of work will be 9.3% of the salary: 40,000 rubles. × 0.093 = 3720 rubles.
As can be seen, for two indicators (“share of production by assortment” and “satisfaction of internal customers”), the results are below the standard. However, the overall result (109.3%) is above the norm, and therefore the employee is given a bonus based on performance.
Thus, the bonus is calculated as a percentage of the official salary, depending on the employee's performance ratio.
The second way to calculate the premium
The total performance bonus is calculated on the basis of the employee's bonus fund as the sum of "private" bonuses earned for each KPI separately. If the size of the bonus fund is known, then the maximum bonuses for all KPIs are first determined depending on their weights:
Then the actual premium for each KPI is calculated as a certain percentage of the maximum premium, depending on how much the actual value of this indicator exceeds the norm:
This formula is applicable only for those indicators for which the "fact" is greater than the "norm". Otherwise, the premium for this indicator is not charged. Then the private bonuses for all KPIs are added up, and the total employee bonus is displayed:
Let's go back to our example. Suppose that the employee's bonus fund is 40% of the official salary, i.e. 40 000 rub. × 0.4 = 16,000 rubles. Then, when using the second method of calculating the bonus, the personal performance table will be different (see Table 3).
Table 3 Premium calculation example (method 2)
|
Key figures |
Weights |
Norm |
Target |
Fact |
Max. premium |
Fact. premium |
|
Volume of production |
5 million rubles |
6 million rubles |
5.5 million rubles |
|||
|
Share of production by assortment |
||||||
|
Share of defective products |
||||||
|
Logistics costs |
90 thousand rubles |
60 thousand rubles |
75 thousand rubles |
|||
|
Satisfaction of internal customers |
||||||
In this case, the maximum bonus for each KPI is determined as a share of the bonus fund in accordance with the weight of this indicator and is accrued upon reaching its target value. For example, for the criterion "output": 16,000 rubles. × 0.35 = 5600 rubles. The same is true for other indicators. In addition, the actual premium for each of them is charged only if the "fact" exceeds the "norm". So, in the above example, for two indicators - "share of production by assortment" and "satisfaction of internal customers" - the standard is not met, so the premium is not accrued. For other indicators, the premium is calculated as follows:

If we add up the actual bonuses for all KPIs, we get the total employee bonus: 2800 rubles. + 800 rub. + 800 rub. = 4400 rubles.
Thus, the premium for each KPI is calculated as a share of the maximum premium, depending on how much the actual value of this indicator exceeds the standard one.
Choice of method
Let's figure out which of the two methods of calculating the premium described above is preferable.
First way - tougher for employees, because it hides a "penalty" for failure to comply with the norm for certain KPIs. If, according to these performance indicators, the result is less than 100%, then the performance coefficient decreases and, as a result, the employee's bonus decreases. Thus, the first way of calculating it stimulates people to a greater extent to pay attention to all indicators, and not just the most important ones. However, it should be borne in mind that the base KPI values should not be overestimated or underestimated. Otherwise, this may lead to the fact that the result (in percent) for these indicators will be inadequately high, if the "fact" turns out to be even a little more than the "norm", or too low - otherwise. It is clear that this will distort the performance ratio. In other words, the range between "base" and "norm" should be wide enough to increase the robustness of the valuation and premium calculation results.
Second way - softer and "democratic", because it does not imply a "fine". As noted above, the premium for indicators for which the norm is not reached is simply not charged.
On the one hand, this is good, because the threat of punishment to many people is annoying and demotivating. In fact, the "penalty" for not meeting the norm is a hidden deduction from the permanent part of the salary, which contradicts one of the basic principles of wages: the permanent salary must remain constant. If the standard is not met, one should not blame the person, but figure out why this happened. After all, in any organization everything is interconnected, and the reasons can be very diverse. And the award should not be a means of punishment for omissions, but an instrument of encouragement for achievements.
On the other hand, this is bad, because employees may simply ignore some indicators that they “do not like”, or do not make any efforts to fulfill their duties if they realize that they are not coping with the standard. Due to the fact that the "automatic" punishment is not included in the calculation of the bonus, the burden on the immediate supervisor increases. To avoid this, the leader must work with subordinates, find out the reasons for low results and motivate people in other ways, primarily intangible.
KPIs are key performance indicators with which you can evaluate the results of the work of employees of various departments of the company. Based on them, employees are promoted up the career ladder or they are paid bonuses.
Relatively recently, company leaders began to actively introduce such a concept as KPI into their work. Now the most valuable thing for which employees work is tied to it - wages. Moreover, the KPI indicator becomes important not only for administration, managers or office employees - line managers, but also for representatives of working specialties.
The main idea of KPI (Key Performance Indicator - usually translated as “key performance indicator”) is that it can be used to unambiguously and objectively evaluate the work and performance of any employee, group of people, department, project and company as a whole. The indicator will reflect the whole picture of the processes taking place in the company, using numbers.
The most important thing is to develop the right KPI for each position and enter real indicators. It is very important for an employee who encounters this concept, having received a job in a company, to immediately understand and understand what exactly is included in his personal set of KPIs (criteria for evaluating his work). The list of indicators will allow the beginner to quickly understand what exactly the employer wants to receive, what results he expects from the employee. The KPI range will immediately show how much effort you need to put in to achieve desired level wages, whether this work will be on the shoulder of the applicant, or, conversely, his abilities will significantly increase the requirements and, accordingly, wages.
Scorecard
The KPI system gives specialists clear work goals and transparent bonuses. But the indicators may turn out to be unattainable, and the transition to such a system can be painful.
In large foreign companies, where everything is spelled out and detailed to the maximum, work on the KPI system is a great option for an employee. He understands how much, for what and when he will receive in excess of the salary. He has personal tasks and deadlines for their implementation, and the company can regularly monitor his work with the help of evaluation.
In many organizations, in addition to the monthly report, it is the KPI results of all employees that serve as the basis for the annual assessment of the performance of the company's personnel. After the annual assessment, the HR Directorate draws up lists of the most promising specialists for enrollment in the company's personnel reserve and promotion.
But if in foreign companies the head office helps in developing goals and indicators, then Russian employers act in a slightly different way. Some invite consultants, others do it on their own: KPI is prescribed by the HR Directorate. Since neither one nor the other thoroughly knows the specifics of the work of each particular specialist, it happens that the indicators are formulated inaccurately. It even happens with us that the most advanced, in quotation marks, organizations for the development of KPI involve managers and employees of the units being evaluated.
Types of indicators
There are some key performance indicators in the KPI assessment system: financial, client, process and development criteria.
To financial indicators include, for example, market value, return on investment - ROI, turnover, cash flow, internal rate of return - IRR, share price, total amount assets and many others. These indicators reflect the external economic condition of the company as a whole.
Customer indicators characterize individual workers who deal with customers and create the external image of the company in the market. These criteria include market share, number of new markets, customer satisfaction, quality, image indicators, and more.
Process indicators include indicators that grow along with the speed of various processes in the company: time to develop and launch new products on the market, processing a client's request; time spent on logistics and delivery of goods, etc.
Development criteria - KPI indicators that characterize the degree and level of development of the company itself (external development processes of the company in the market and internal development processes human resources): staff productivity, profit or administrative costs per employee, staff satisfaction level and its "churn".
The employee works as a consultant in the sales department, answering questions from potential buyers by phone. The following key performance indicators (KPIs) are defined for it: customer satisfaction and the number of purchases that people made after consulting an employee over the phone.
Advantages and disadvantages
The KPI system is good for employees whose work results affect the financial and economic performance of the enterprise. In trading firms, these are, first of all, top managers and sales managers, in recruiting companies - recruitment consultants.
In some companies, the performance of an employee's KPI also affects the individual size of the annual salary review: the higher the score, the higher the percentage of salary growth. For example, the annual bonus for managers may consist of two variables that depend on the results of meeting individual goals and on the performance of the company. This approach encourages better performance of functional duties.
For employees from different departments, the size of the bonus, which is affected by KPI, can range from 20 to 100 percent of salary. At the same time, the formula for accruing the bonus itself is quite complicated: it takes into account the number of KPIs, the coefficient of completion of each of them, as well as its “weight”, called the coefficient of influence.
If the KPI scale is compiled incorrectly, there will be little benefit from it. If there are too many KPIs, the impact of each on the amount of the total bonus will be small. For example, initially there were about 20 percent of KPIs, but a year later they were reduced to five. Most of the indicators accounted for a small share of the bonus, and the loss of 5 percent in it is not particularly significant. A 20% KPI weight motivates much more effectively.
One of the main disadvantages of the KPI system is the dependence of the quality of work of an individual employee and the performance of the entire department. If the unit did the work poorly or not quite qualitatively, without fulfilling the general plan, then all employees of the department can lose their salary at once. After all, personal KPIs are associated with key indicators of the entire department. In case of systematic non-fulfillment of planned indicators, an employee may be demoted or dismissed. Therefore, KPI forces you to always "be in shape and tone." Who can not stand this rhythm, leaves himself.
Another disadvantage is that not all employees can directly influence the company's strategic KPIs. When the bonus depends on net income and sales, the secretary or economist will not be able to influence it.
From experience it can be said that very often in Russian companies the KPI motivation system is one-sided: everything that an employee overfulfills is just a job well done, for which he receives a salary, and for underfulfillment he is deprived of some part of his salary.
Many managers international companies think that work technical specialists(accountants, engineers, programmers) easier to describe job description than prescribing KPIs for them. We must not forget that the planning and calculations of this system take time. Heads of areas or departments at the end of each month spend time setting and calculating KPIs for all their subordinates. The indicators have to be coordinated with the HR department, and the main work of managers goes by the wayside, and after all, bosses have their own KPI.
As a rule, the transition to a KPI system is usually accompanied by unrest in the team: some quietly sabotage it, others completely do not accept it and leave the company. It is difficult to immediately change your habits, the order in which functions are performed, and get used to the new conditions of remuneration. It is easier for new employees if the HR manager explains to them in an accessible way what the company pays bonuses for, and newcomers, most likely, will normally perceive work according to such rules.
Opinion 1:
Ludmila Shusterova, Deputy CEO BDO outsourcing division
Original KPIs
KPIs are usually associated with either an increase in the profitability of the company and its turnover, or with an increase in productivity and efficiency in the use of capital assets. Based on these conditions, it is unlikely that it will be possible to draw up some fundamentally new and original KPIs. Unless, of course, the work is connected with something very non-standard. For example, you can put an increase in the number of koalas by n percent in the KPI for the head of a biological station. But for a typical manager, it is unlikely that anything better will come up than an increase in revenue, margins, increased customer satisfaction, or a decrease in staff turnover. It is desirable that there are several KPIs, but not too many. Indeed, in the pursuit of business and profit growth, it is important that both customers and staff do not suffer - and this is not a trivial task at all.
But the main task indicators - to be not original, but effective.
Opinion 2:
Dmitry Pelah, Director of the Financial Consulting Agency
Regulation on KPI
In order to start applying the KPI system in your company, you need to fix it in internal documents. A regulation on KPI should be developed, which will be approved by the head of the company. In this position, it is desirable to provide formulas and calculations on the basis of which the system of indicators is built. It is also important to link indicators to data. accounting or with IFRS if the company uses international standards.
The regulation on the KPI system should establish a causal relationship of indicators with the main goals of the company and determine the level of responsibility for the values of the indicators of employees to whom this system will be applied.
There is no standard form for a KPI statement, so a company can develop it on its own or seek help from specialized consulting firms.
Opinion 3:
Ivan Shklovets, Deputy Head Federal Service for work and employment
Dismissal for low performance
Such grounds for dismissal as a low performance indicator, labor law does not contain. Therefore, the employer has no right to dismiss an employee with such a wording.
It is possible to dismiss an employee due to inconsistency with the position held only based on the results of the employee's certification, which must be carried out in the manner established by the employer himself in the form of a local normative act. In this case, there must be a protocol attestation commission. However, even in this case, before dismissal, the employer will be obliged to offer the employee other available vacant positions or the work that he can do, taking into account his state of health.
Non-compliance by an employee with established labor standards or quantitative (qualitative) indicators may affect the amount of remuneration. For example, incentive payments may be reduced or canceled. However, when working out the established norm of working time, the employee in any case will have a guaranteed right to receive the salary established for him ( tariff rate). If the employer nevertheless dismissed the employee on the above grounds, he has the right to appeal such dismissal in court.
Pros and cons of using KPI to evaluate employee performance
|
pros |
Minuses |
|
The amount of an employee's bonus directly depends on the fulfillment of his personal KPI |
Due to too many KPIs in the total bonus, the share of each of them is small |
|
Each employee is assigned responsibility for a specific area of work. |
Too much weight of one of the indicators leads to distortions in work (the employee does not pay enough attention to the functionality that has the least weight in the KPI system) |
|
The employee sees his contribution to the achievement common purpose companies |
Really unattainable KPIs demotivate employees |
Articles in this section
- Proper incentives for employees
The topic of motivating and stimulating the work of employees is one of the key issues of personnel management in any organization. When establishing a system for stimulating the work of employees, it is important to prescribe all the necessary provisions in local acts. Otherwise, the claims of the inspectors are possible.
- Motivations
What are the practices for rewarding and recognizing employees in your company? Is there a unified approach/general culture of gratitude and support for the initiative of employees, or does it all depend on the individual style of managers?
- Staff motivation. Fight for efficiency. It's time to act!
A crisis, whether internal or external, forces people to learn and companies to change. As long as the company is profitable, and there is no hint of problems, the owner and director are unlikely to be ready for major changes. Poor performance in business (like…
- Individual promotion of employees. How?
Individual system Encouraging employees is an integral part of the work of an HR manager. After all, a productive employee is, first of all, a satisfied employee!
- We motivate accountants
Not all key performance indicator systems are capable of making accountants perform their duties more efficiently and efficiently. However, everything can change if you connect the gameplay to the motivation.
- Formation of a system of non-material incentives
At present, all possible systems of material incentives are developing quite well at enterprises. This is due to the fact that employers seek to clearly define and subsequently know for what, for what specific work he pays the employee ...
- Employee Motivation: The Equity Model
If employees perceive remuneration as fair, their labor contribution remains approximately at the same level. The biased attitude of management initiates the emergence of tension and motivation aimed at reducing the degree of injustice. If employees perceive remuneration as too high, equity theory states that they will feel an imbalance in their relationship with the employer and seek to restore the balance.
- How Motivational Factors Work
How to build the practice of personnel management in your company based on the theory of motivation, read the article.
- Is a counteroffer in the labor market a way to keep a specialist in a company?
Recruiters at recruiters say that employers are increasingly resorting to counter-offering (i.e., offering better terms than the new employer) in an attempt to retain a good employee who has already decided on a new job and is leaving. How relevant is the counterproposal today? Many companies are not only not retaining employees, but on the contrary, they are reducing staff. Nevertheless, the topic of the counterproposal remains relevant to this day, because good specialists or leaders are needed always and everywhere. Accordingly, accepting or not accepting a counteroffer is one of the defining choices in a person's career. After all, which offer you choose will depend on your further fate as a specialist or as a leader. You will learn about what is happening in the labor market now from the article
- Motivational profile of the candidate
- What do TOPs who already have everything want?
The question "How to motivate someone who already has everything?", from my point of view, is an epic. What is the difference between a true story and an epic? A true story is a story that happened once, and an epic is a repetition of this story many times with distortions in legends and myths. That top manager who already has everything has never met in my life, this is an epic.
- The most effective methods of staff motivation
Employees should be stimulated on intermediate achievements, without waiting for the completion of all work, since great successes are difficult to achieve and relatively rare. Therefore, it is desirable to reinforce positive motivation through not too large intervals of time. It is important to make employees feel confident, because this is required by the internal need for self-assertion. Success brings success. In general, it is possible to formulate a number of rules for the effective motivation of employees.
- Diagnostics of motivation
The article is devoted to the study and evaluation of the strategic development of the system for managing the motivation of the labor activity of managers and specialists, as well as their remuneration at the enterprises of the construction complex of the Penza region. The possibility of existence of unused managerial reserves in strategic system work motivation.
- satiety threshold.
Managers are characterized by territorial mobility, high sensitivity to changes in the labor market and are not limited to a specific geographical area. They live and work throughout the space Russian Federation. At the same time, there are pronounced local features that significantly distinguish, for example, a information technology the city of Voronezh from the same specialist in the city of Yekaterinburg. The differences come down to three main parameters: the size of the "satiation threshold", the format of leisure activities and self-esteem.
- Job Satisfaction as a Component of Effective Organizational Behavior
The most important task facing the modern Russian business community is the development of mechanisms for managing the organizational behavior of an employee. Organizational behavior will be effective if it contributes to the achievement of the strategic goals of the organization, i.e. the main vector of behavior of all employees coincides with the movement of the organization to achieve its strategic goals. However, the achievement of these goals will be possible only if this movement is sustainable. Job satisfaction (job satisfaction) can give such stability to the behavior of employees.
- Motivational mechanism of corporate culture
Perhaps the key condition for increasing the efficiency of the internal segment of corporate management remains the choice of adequate methods for activating personnel at all levels of the hierarchy: from an ordinary performer to a top manager.
Why, in an atmosphere of budget cuts and staff cuts, some employees are loudly indignant, while others are quiet? Does this mean that the former began to work worse? How demotivated are the “quiet ones” who are completely withdrawn into themselves? This article briefly describes a little-known, but very effective for business model of personal differences by W. Marston DISC, explains why different people react and behave differently in a crisis, gives recommendations on the individual motivation of representatives various types personality.
- Don't you have exactly the same, only without wings?
In job advertisements, you can often read the following: "Sociability, initiative, discipline and creative thinking - the necessary conditions". Of course, we all want "everything and a lot", not assuming that some requirements may be incompatible.
Why when developing employee incentive programs it is necessary to focus on strategic goals companies?
How to make the motivation system as transparent as possible? - How to motivate staff in a crisis
The crisis situation threatens the company not only with financial problems and the loss of its positions in the market, but also with the loss of qualified personnel, without which it is impossible to overcome the crisis. Retention of key employees is one of the main tasks of management at the crisis stage, and this goal can be achieved if the staff is informed in a timely manner and an adequate motivation system is implemented. Let's talk about this in more detail.
The article discusses the motivation factors that most often cause employees to change jobs. Given practical advice and advice on how to eliminate and/or reduce the negative impact of these factors or reduce the risk of their occurrence.
